The Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention of This Bacterial Infection
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that affects the throat and tonsils. The bacterium that is the cause of strep throat is known as Streptococcus Pyogenes or commonly known as Group A Streptococcus (GAS). Group A bacteria is the type of bacteria that is found in the nose and/or mouth.
A person of any age can contract strep throat, however, it is most common in kids of school age and teenagers – those primarily between the ages of 5 and 15 years old. A person with their tonsils removed can still contract strep throat as this bacterial infection is very contagious.
Since strep throat is quite contagious it can quickly spread through a large group of children and teenagers that come in contact in close quarters – in places such as school buses, classrooms, dorms, childcare facilities, family households, etc. This infection can be spread quite easily via the airborne droplets from a cough or sneeze from the infected person. The strep bacteria can live for a short period of time on doorknobs or surface areas. An unaffected person can contract strep throat by coming in contact with a doorknob or surface area that contains this bacterium and then touch his/her nose, eye, or mouth area.
Strep throat usually occurs in late fall and early spring. It is estimated that there are over 600 million cases worldwide of strep throat each year.
Keep in mind, not every sore throat is actually strep throat. Only a small portion of sore throats are actually diagnosed as strep throat. There are several things that can cause a sore throat, such as allergies or viral infection (whereas strep throat is a bacterial infection).
Symptoms
Symptoms of strep throat include: Sore and/or scratchy throat; difficulty swallowing; swollen lymph glands; patches (either red or white in color) that develop in the back of the throat or roof of the mouth; cough; hoarseness; fever; headache; rash; stomachache; nausea; vomiting; and fatigue. In some cases, throat pain may be so severe that it results in either drooling or dehydration due to the inability to swallow.
The above-mentioned symptoms associated with strep throat vary depending on the age of the person that has contracted the illness. Infants and children under the age of three years may experience nothing more than low-grade fever, sore throat, and decreased appetite. Children over the age of three years through the adolescent years generally experience the worst of the symptoms associated with this illness tending to have high fevers and severe sore throats. The strep throat symptoms experienced by adults vary – they may be very mild or severe.
If you have been around someone with strep throat and exposed to the germs, symptoms usually occur within a period of three days. If you suspect strep throat, contact a doctor for accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment. Research shows that treatment started within the first 48 hours after symptoms occur reduces the length of the symptoms by one or two days.
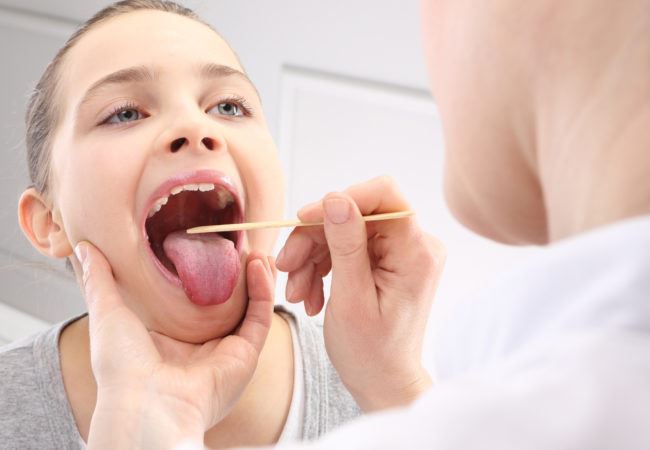
If a doctor suspects strep throat, he/she will exam the throat for swelling or redness and check for fever and enlarged lymph glands. If the doctor continues to suspect strep throat based on the results of the physical examination, they may proceed with a test to confirm. This test may be a rapid strep test kit (also referred to as a RADT or Rapid Antigen Detection Test). This test consists of a cotton swab used to swab culture from the throat and tonsil area. This rapid strep test kit provides results within a few minutes and is considered 95 percent accurate. If the results of the rapid strep test kit show negative for strep throat, a medical professional may also order a throat culture to make sure. Where the rapid strep test kits are considered 95 percent accurate, a throat culture is considered 100 percent accurate in diagnosing strep throat.
Though strep throat itself is not considered particularly dangerous to one’s overall health, it can become dangerous to your health without treatment. With medical diagnosis and treatment, the symptoms of strep throat are usually better in a period of one week. If left untreated, strep throat has the potential of causing complications such as inflammation of the kidneys, middle ear infection, pneumonia, meningitis, acute, rheumatic fever, and scarlet fever among others. It is also possible for an individual with a healthy immune system to recover from strep throat without any medical treatment and no complications. The severity and duration of the symptoms associated with strep throat are lessened with taking prescribed antibiotics.
A person with strep throat is considered contagious 24 to 48 hours after antibiotic treatment begins. If a person with strep throat is not treated with antibiotics they may be contagious up to a period of three to four weeks even if they are no longer experiencing symptoms.
Treatment
There is no vaccine that prevents someone from contracting the bacteria that causes strep throat. Your odds of contracting strep throat increase greatly if you are exposed to someone carrying this disease that has not been treated with antibiotics. The primary methods of prevention are the same as those for cold – good hygiene. The frequent and thorough washing of hands; covering the nose and mouth when sneezing or coughing; and not sharing food, drink, or eating utensils can reduce the chances of contracting strep throat.
Fortunately, the bacteria associated with strep throat (Streptococcus pyogenes or as group A streptococcus) is highly responsive to antibiotics. Often a doctor will prescribe either penicillin (or a derivative of penicillin such as amoxicillin) in either an oral or injectable form. In addition to the medication, the doctor will recommend rest and avoiding exposure to chemicals that may irritate the throat. The doctor may also prescribe an analgesic (a non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug) to help with pain, or they may also recommend taking Advil, Motrin, or Tylenol to address associated symptoms.
In many cases, doctors will prescribe antibiotics to the entire family when a family member is diagnosed with strep throat to prevent the illness from spreading through the household.

